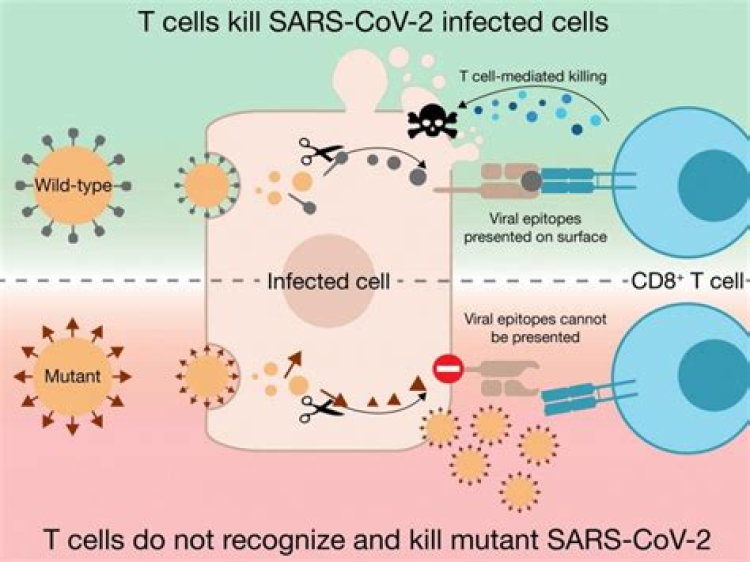
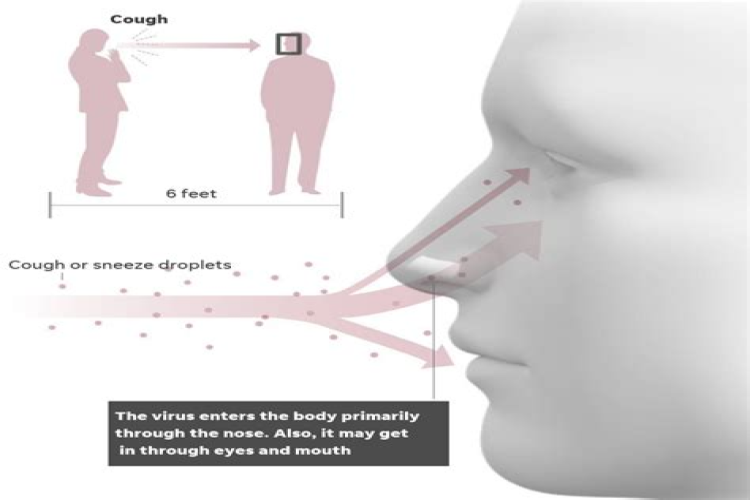
Antibody-dependent enhancement
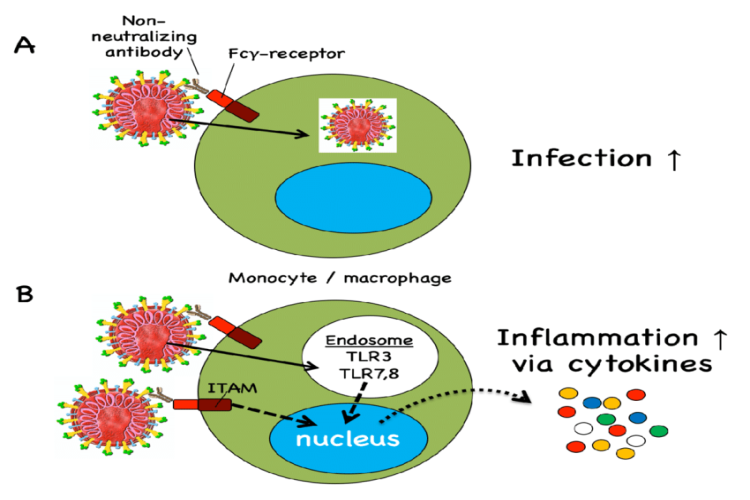
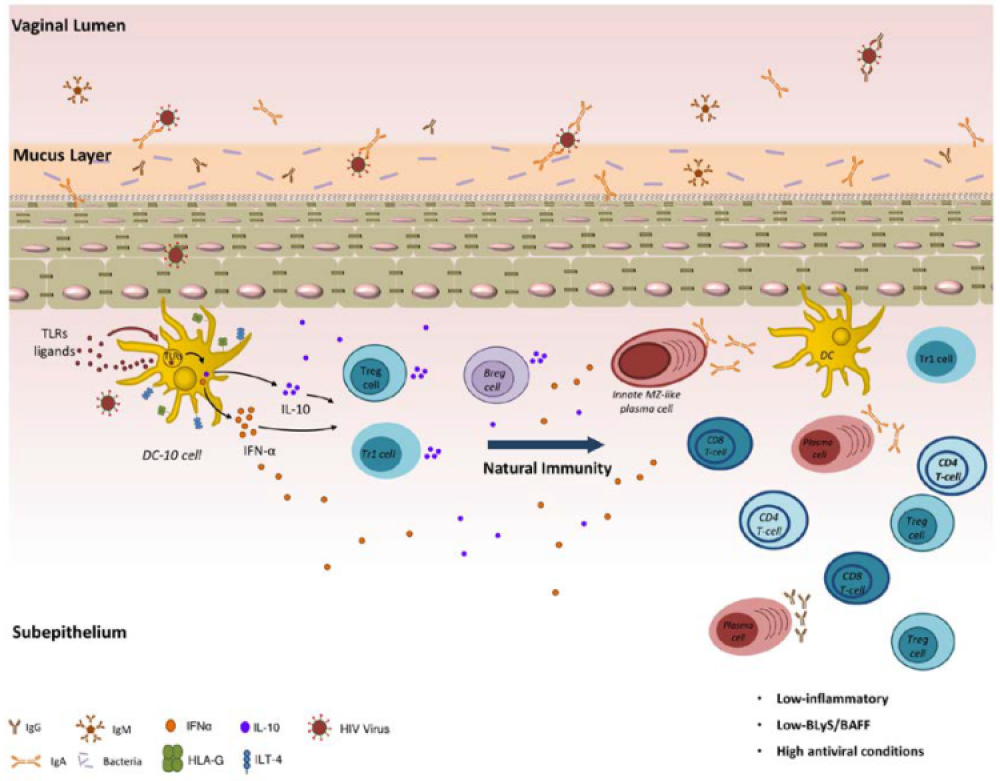
Antibody-dependent enhancement (ADE), sometimes less precisely called immune enhancement or disease enhancement, is a phenomenon in which binding of a virus to suboptimal antibodies enhances its entry into hostcells, followed by its replication.[1][2] ADE may cause enhanced respiratory disease and acute lung injury after respiratory virus infection (ERD) with symptoms of monocytic infiltration and an excess of eosinophils in respiratory tract.[3] ADE along with type 2 T helper cell-dependent […]