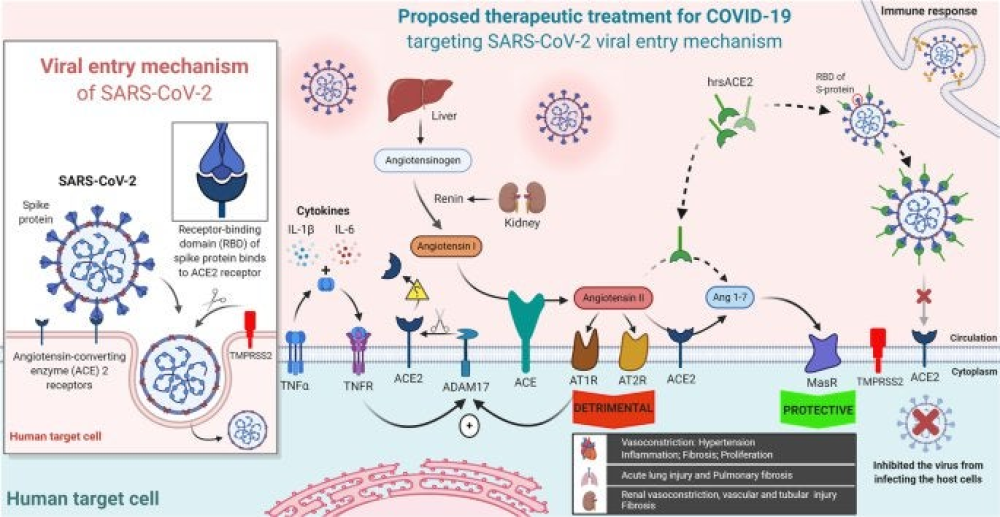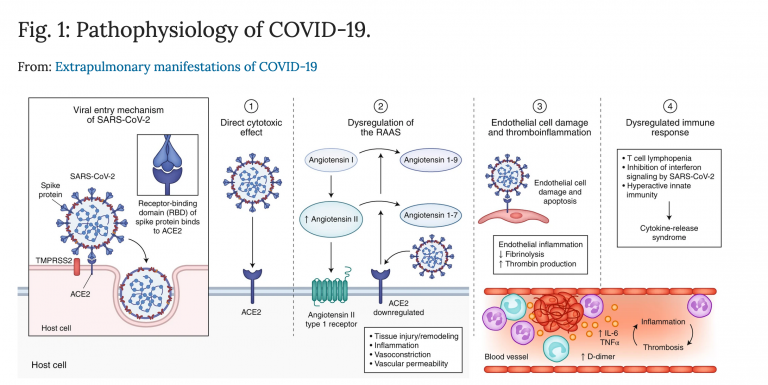
Could tiny blood clots cause long COVID’s puzzling symptoms?
Scientists debate evidence for a micro-clot hypothesis that has some people pursuing potentially risky treatments Authors: Cassandra Willyard Nature 608, 662-664 (2022)doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-022-02286-7 When Lara Hawthorne, an illustrator in Bristol, UK,…[...]
Read More