Authors: Si Zhang 1, Yangyang Liu 2, Xiaofang Wang 2, Li Yang 3, Haishan Li 4, Yuyan Wang 5, Mengduan Liu 2, Xiaoyan Zhao 2, Youhua Xie 5, Yan Yang 6, Shenghui Zhang 7, Zhichao Fan 8, Jianzeng Dong 2, Zhenghong Yuan 5, Zhongren Ding 2, Yi Zhang 9, Liang Hu 10
Abstract
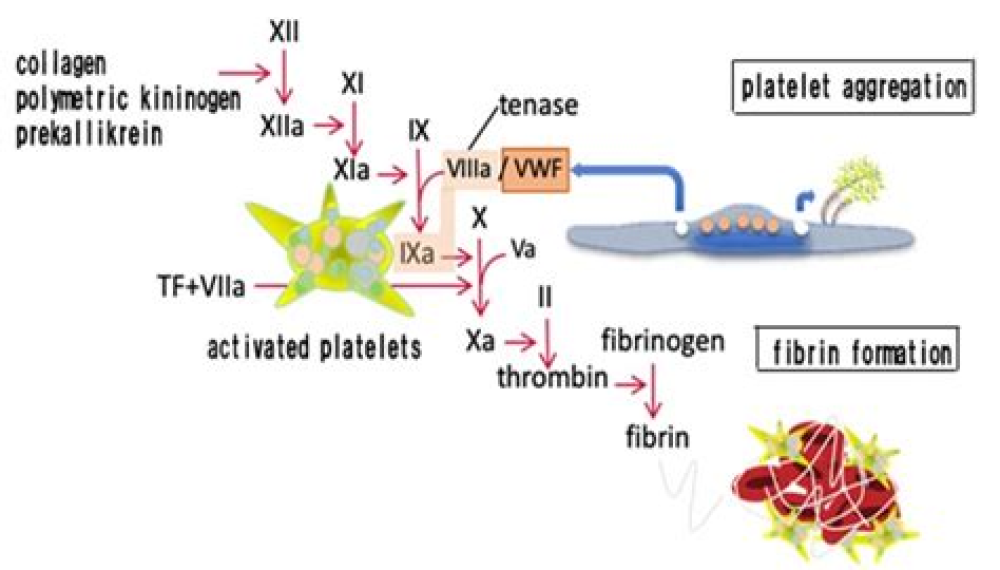
Background: Critically ill patients diagnosed with COVID-19 may develop a pro-thrombotic state that places them at a dramatically increased lethal risk. Although platelet activation is critical for thrombosis and is responsible for the thrombotic events and cardiovascular complications, the role of platelets in the pathogenesis of COVID-19 remains unclear.
Methods: Using platelets from healthy volunteers, non-COVID-19 and COVID-19 patients, as well as wild-type and hACE2 transgenic mice, we evaluated the changes in platelet and coagulation parameters in COVID-19 patients. We investigated ACE2 expression and direct effect of SARS-CoV-2 virus on platelets by RT-PCR, flow cytometry, Western blot, immunofluorescence, and platelet functional studies in vitro, FeCl3-induced thrombus formation in vivo, and thrombus formation under flow conditions ex vivo.
For More Information: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32887634/